T6: Propagating sound waves:
sound speed and interference
Before the tutorials:
Think about:
- What are waves?
- What is the difference between a longitudinal wave and a transversal wave?
- What is the sound speed of a medium?
- What is the Amplitude of a wave?
- What is the wavelength?
During the tutorials:
To run the experiment, we first need to
- Create a slab with uniform distribution of particles (say 200x10x10)
- Initialize a sound wave
Now we can perform the simulation and analyze it.
- When compiling the code, do not forget to switch on
PERIODIC and
NOGRAVITY again. Also you have to indicate the non quadratic form
of the simulation domain by setting LONG_X=20,
LONG_Y=1 and LONG_Z=1
in the Config.sh file before compiling.
- When setting proper values in the file
box.param, do not
forget to also set PeriodicBoundariesOn 1 again, before running the simulation.
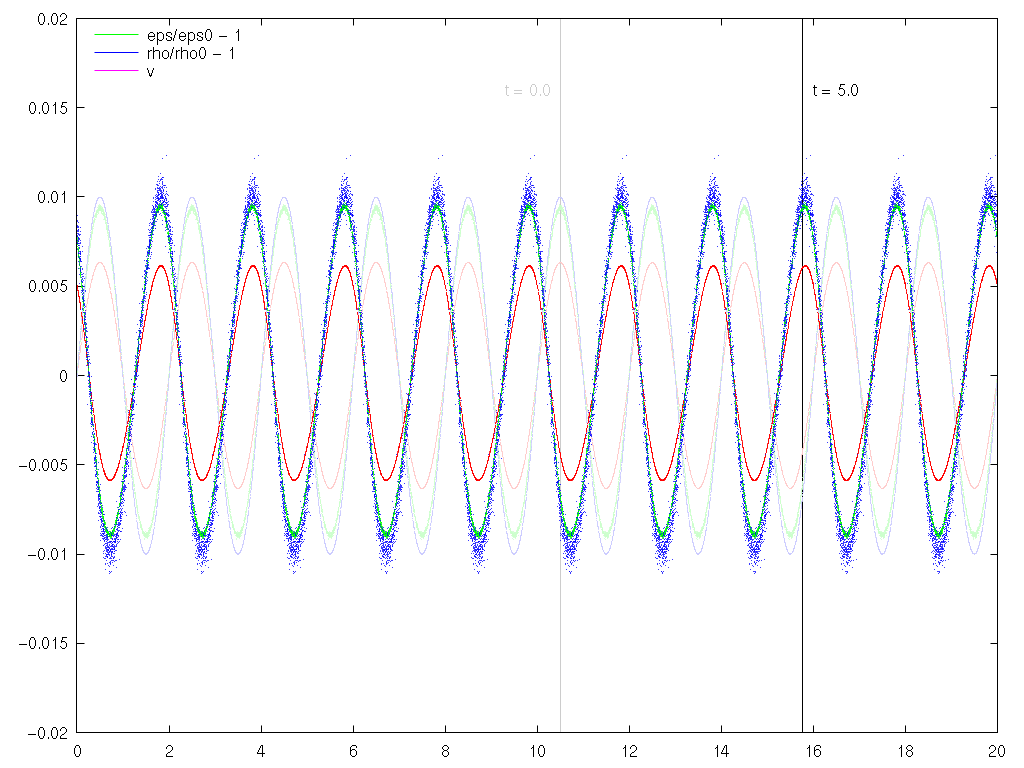
- Verify that the perturbation propagates with the sound speed.
- Verify that the propagation speed does not depend on the amplitude of the wave.
- Check what happens if you increase the wavelength.
Programming goals for T6:
Again, we are producing different initial conditions and run simulations on non-cubic domains,
especially we will
- glue together particle distributions to create a slab-like region
- set up some initial perturbation
- use MPI or OpenMP parallel features to speed up the code. Watch what the programs says at the beginning:
Running on 1 MPI tasks
Using 1 OpenMP threads
you can change this by:
-
export OMP_NUM_THREADS=4
which should then display like:
Running on 1 MPI tasks
Using 4 OpenMP threads
-
mpirun -np 4 OpenGadget3/P-Gadget3 box.param
which should then display like:
Running on 4 MPI tasks
Using 1 OpenMP threads
Solutions
- Examples for a script to create a larger box of particles out of the small example patches
from T03 and to place different perturbation in it.
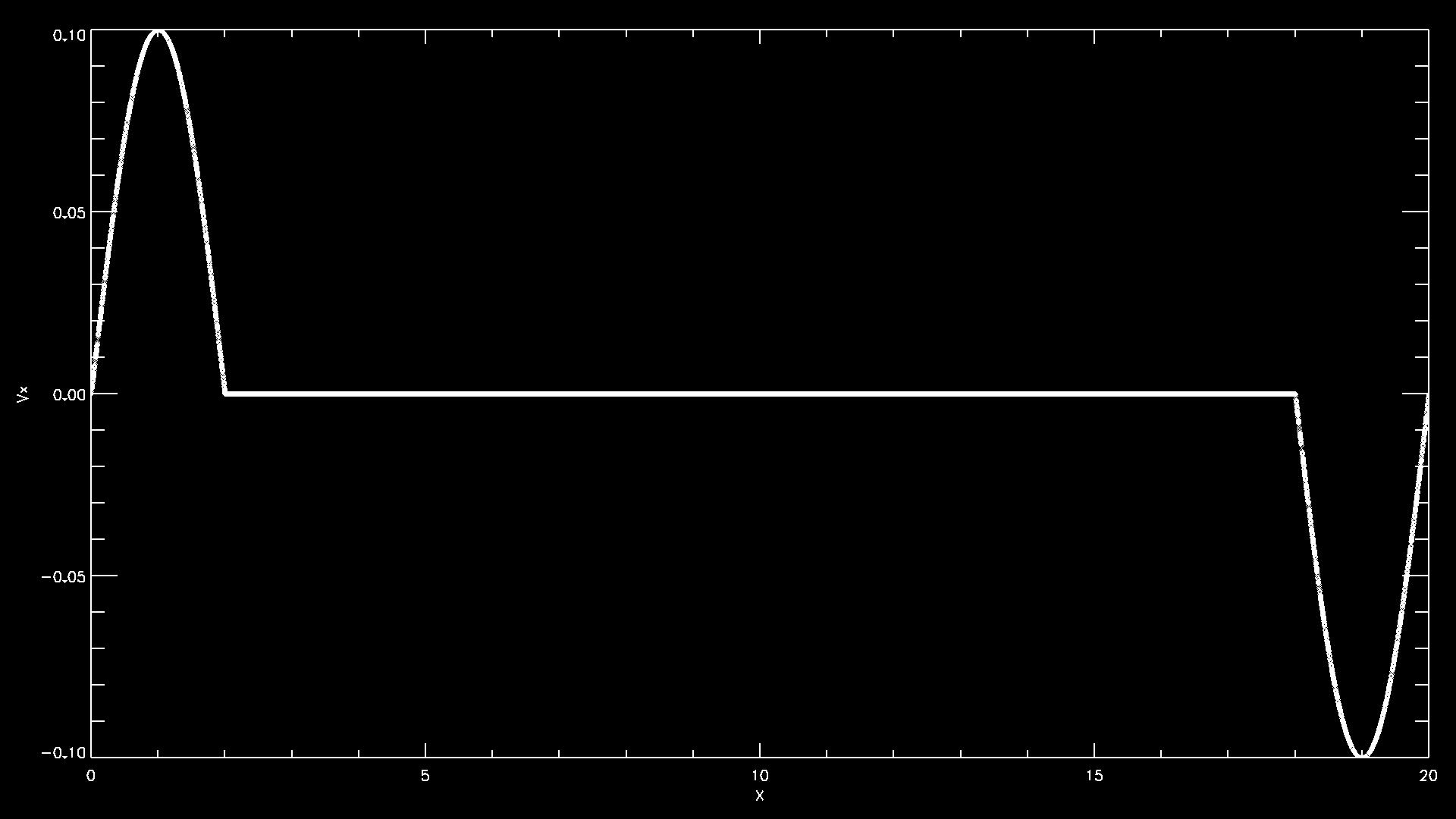
- Examples for a the initial velocity perturbation
- Examples for a script to show the time evolution
- Examples for the propagation of a longitudinal wave
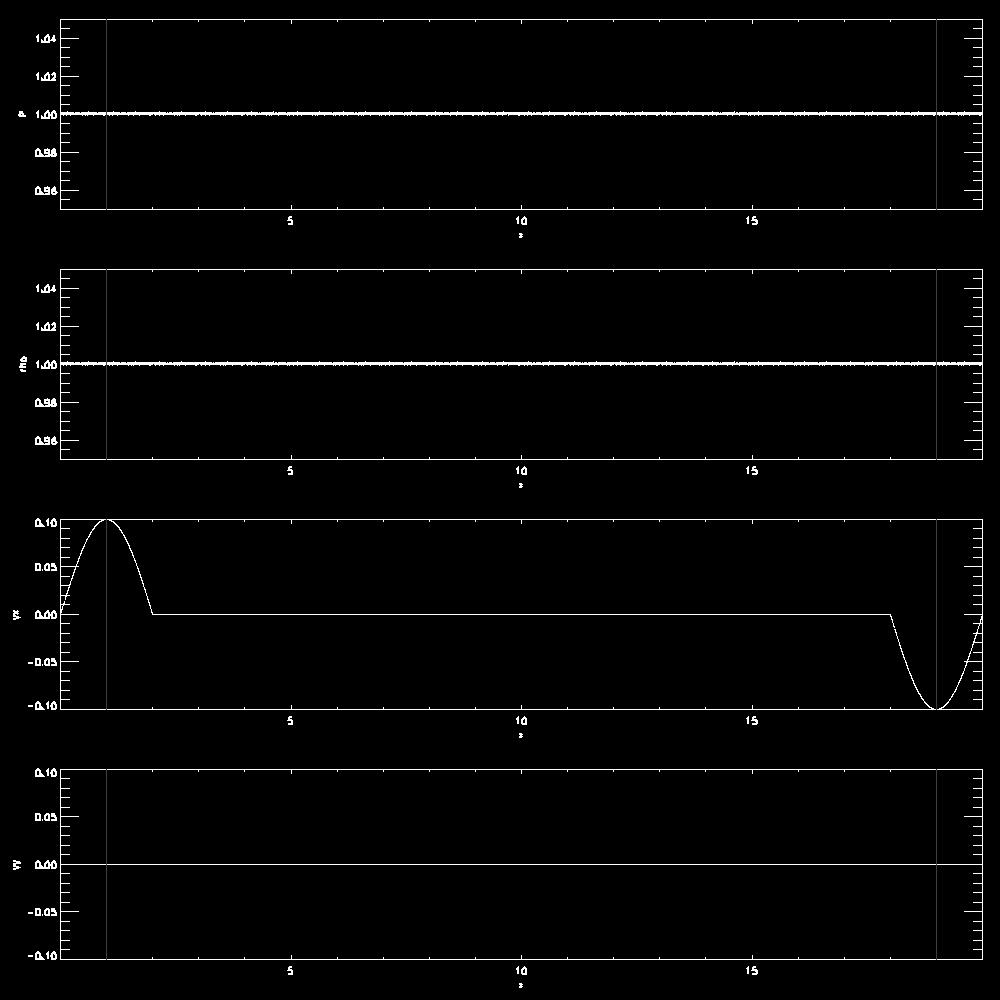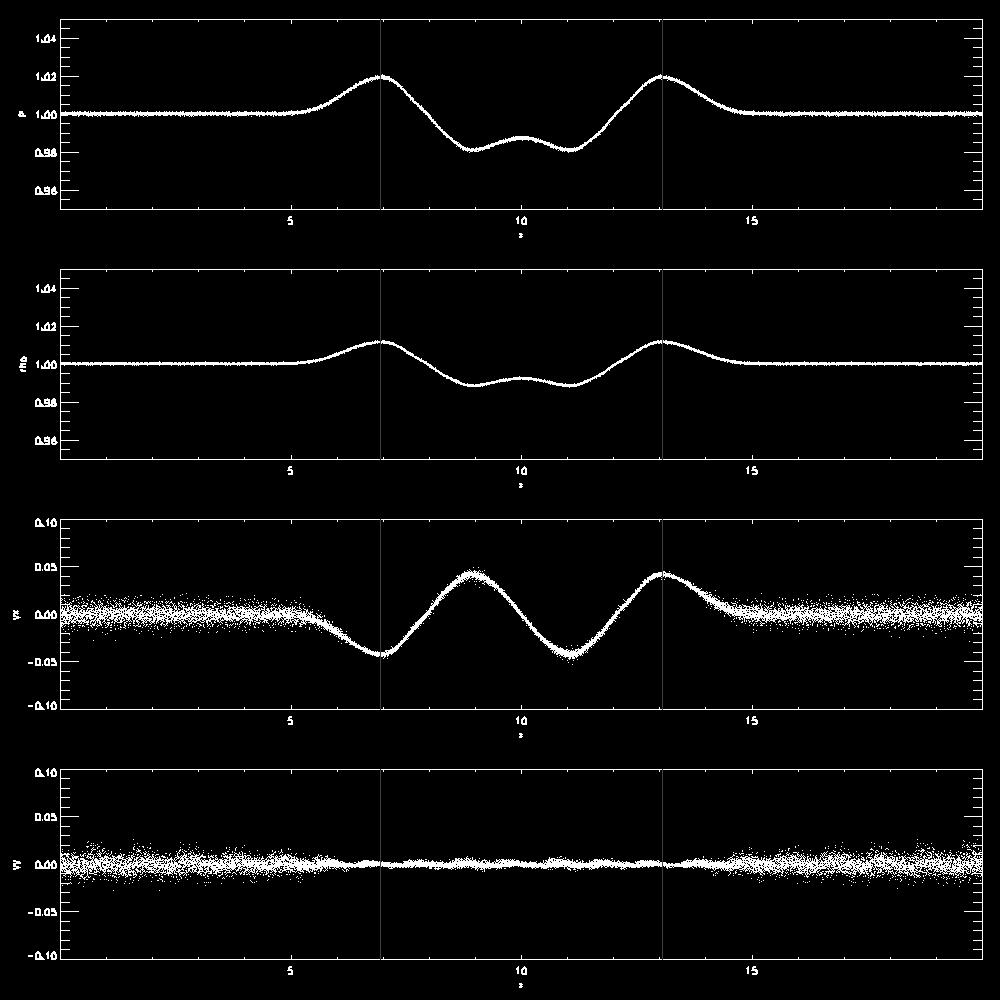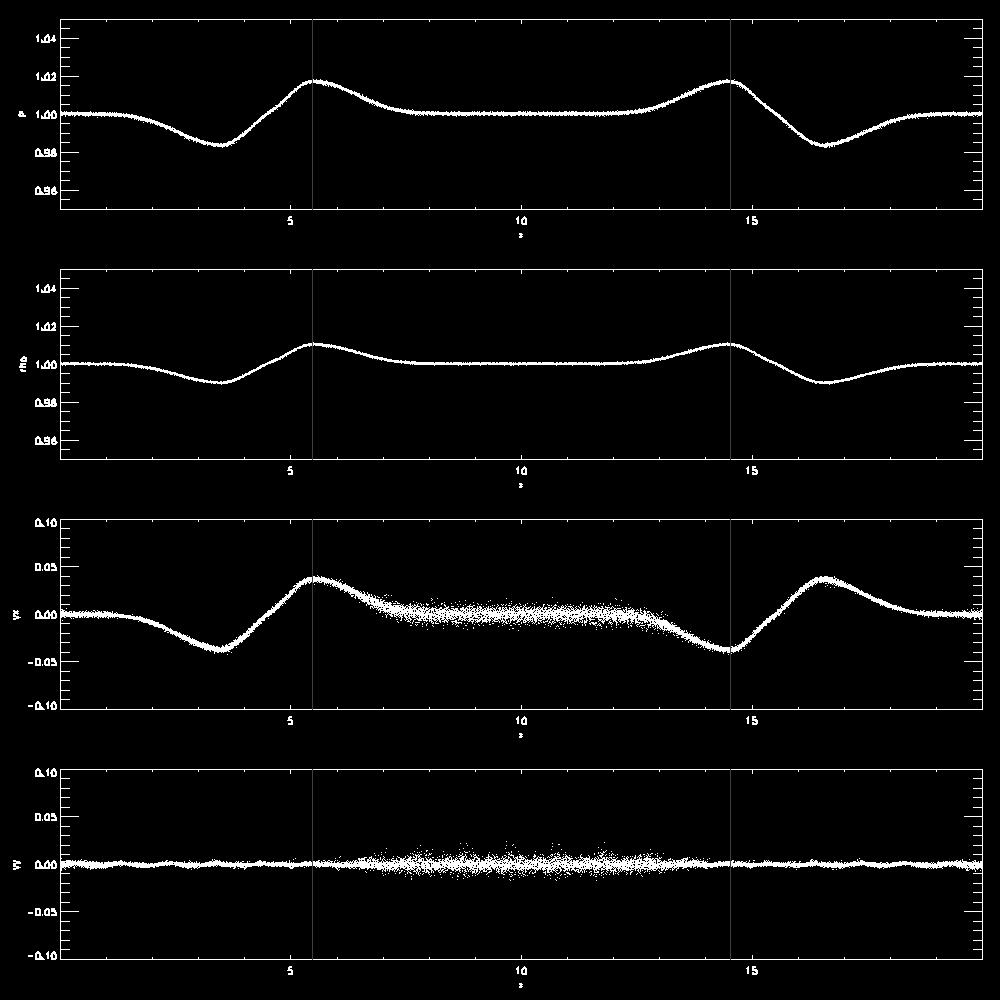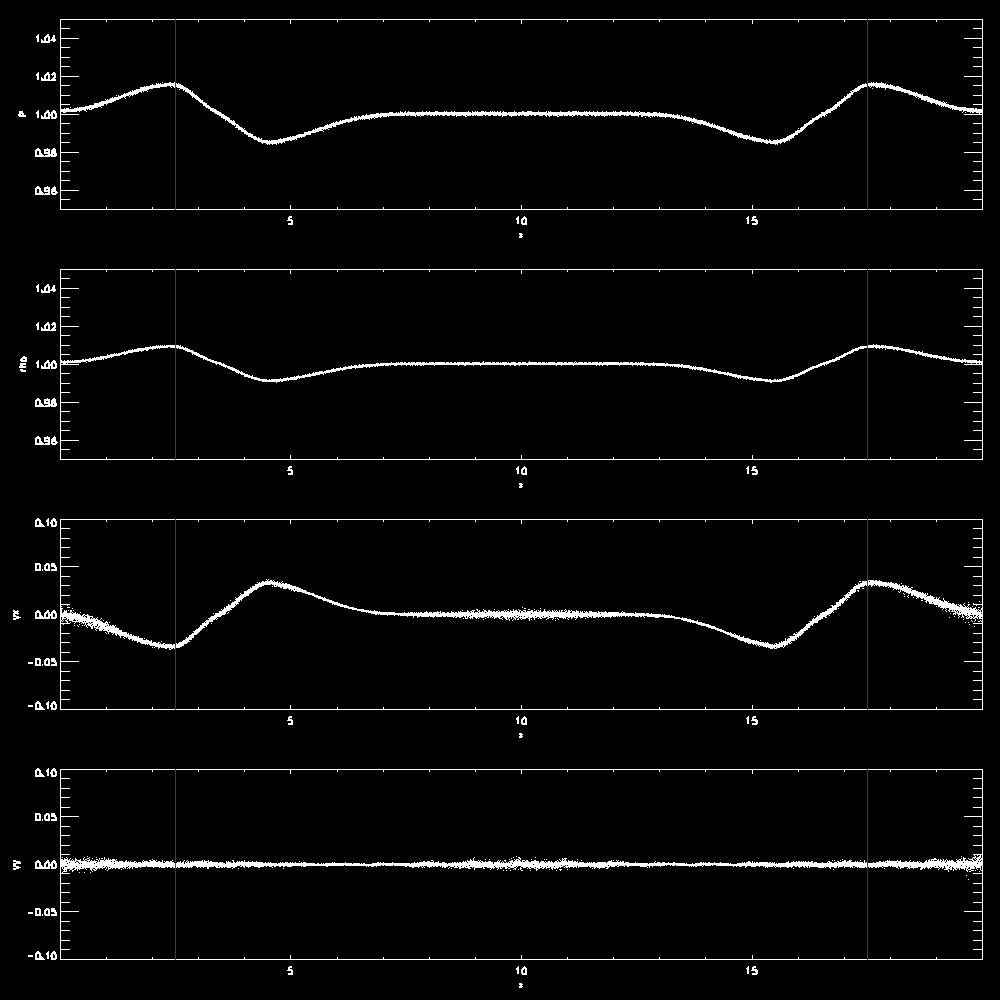
- Examples for a transverse wave
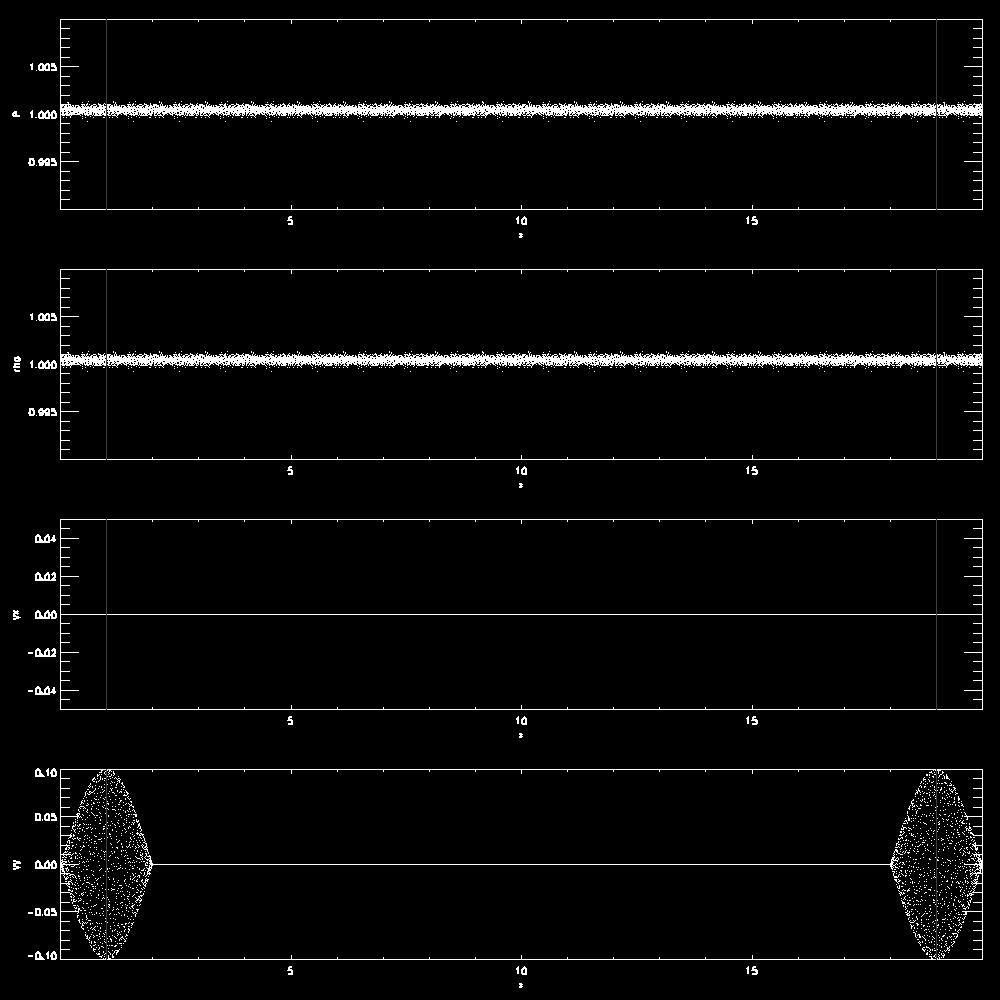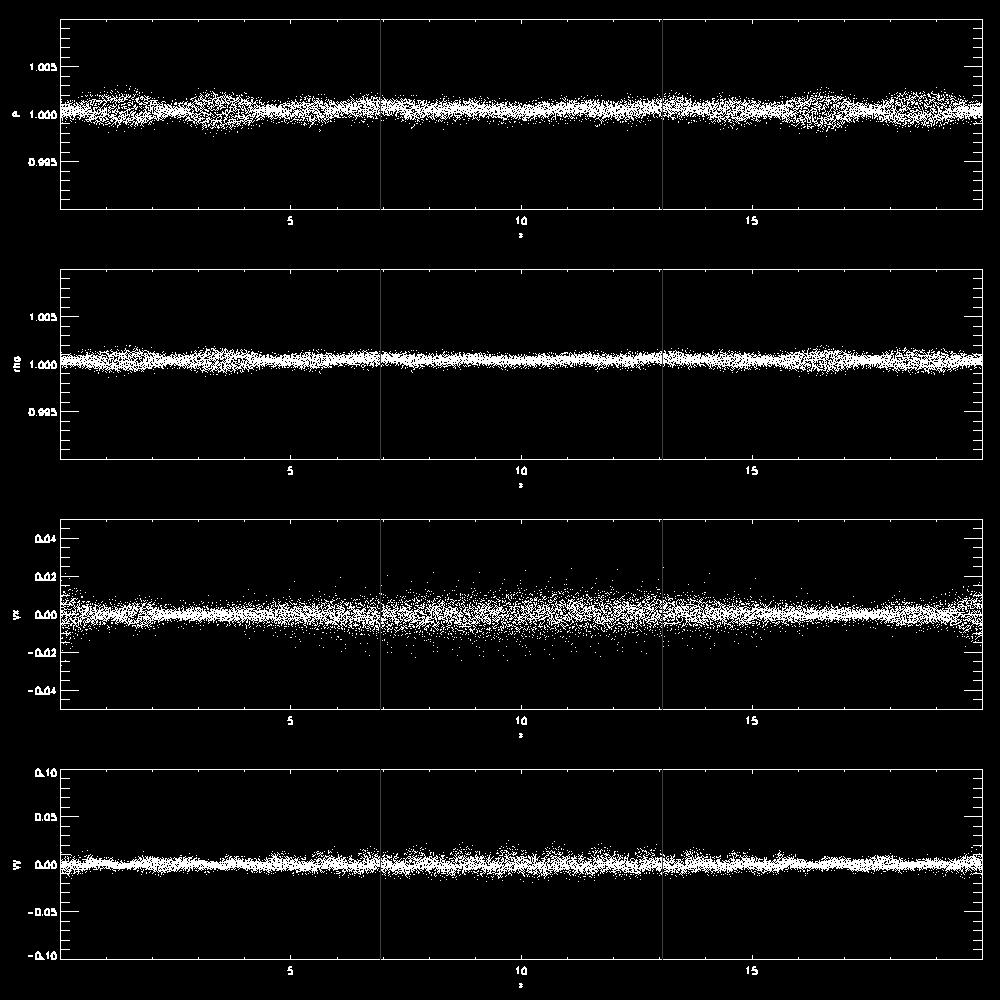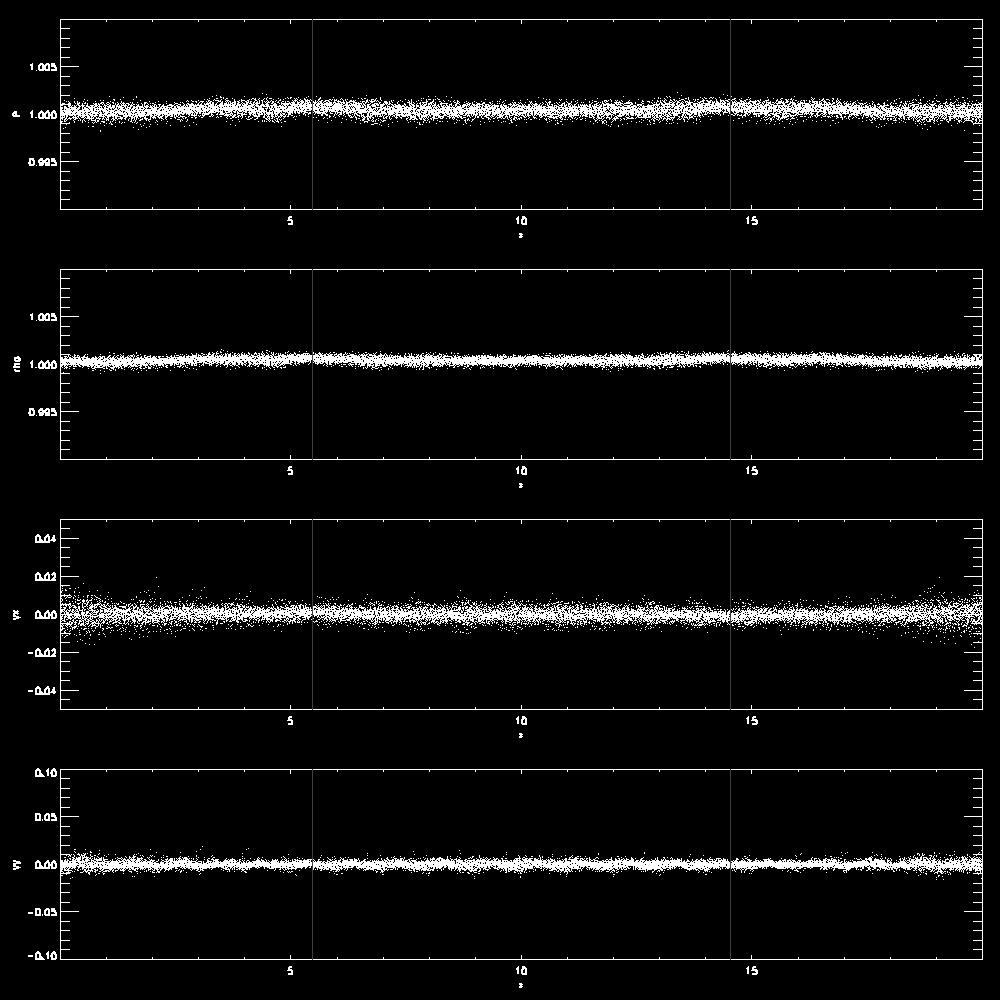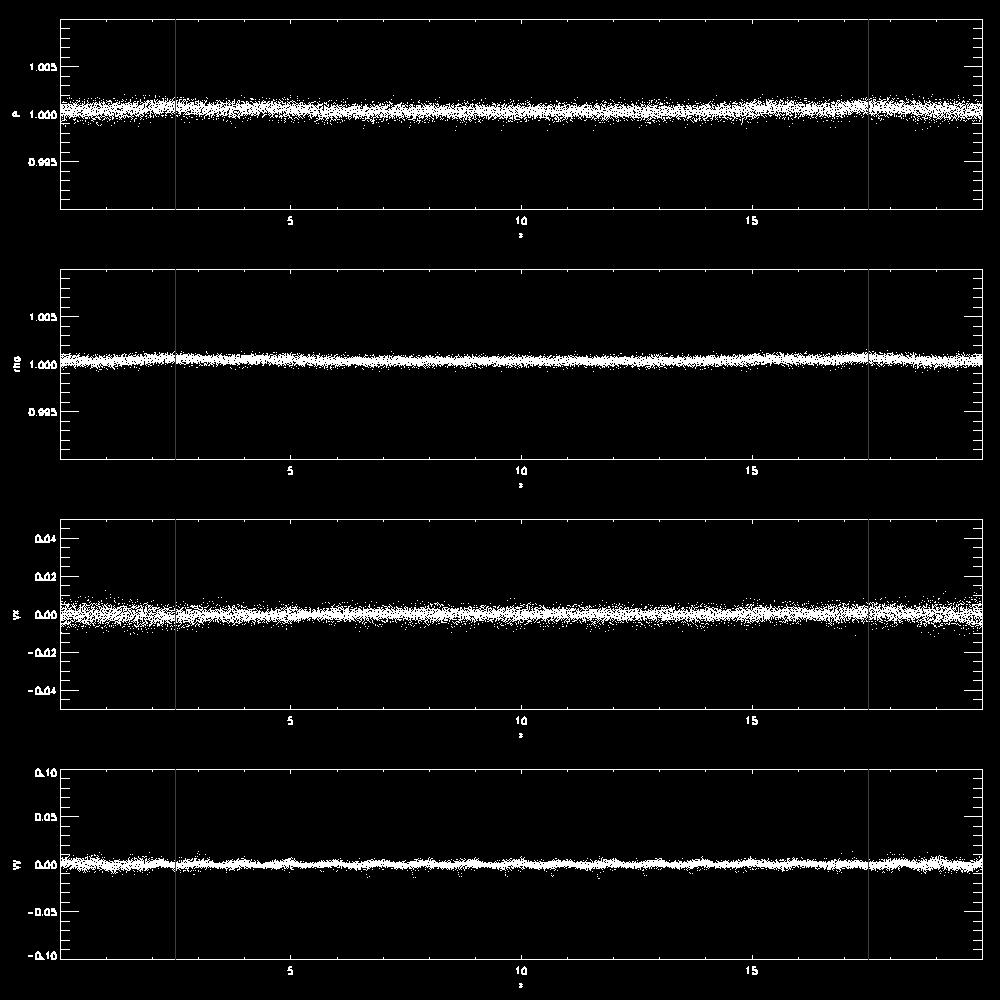
- Examples comparing waves with different wavelength or amplitudes
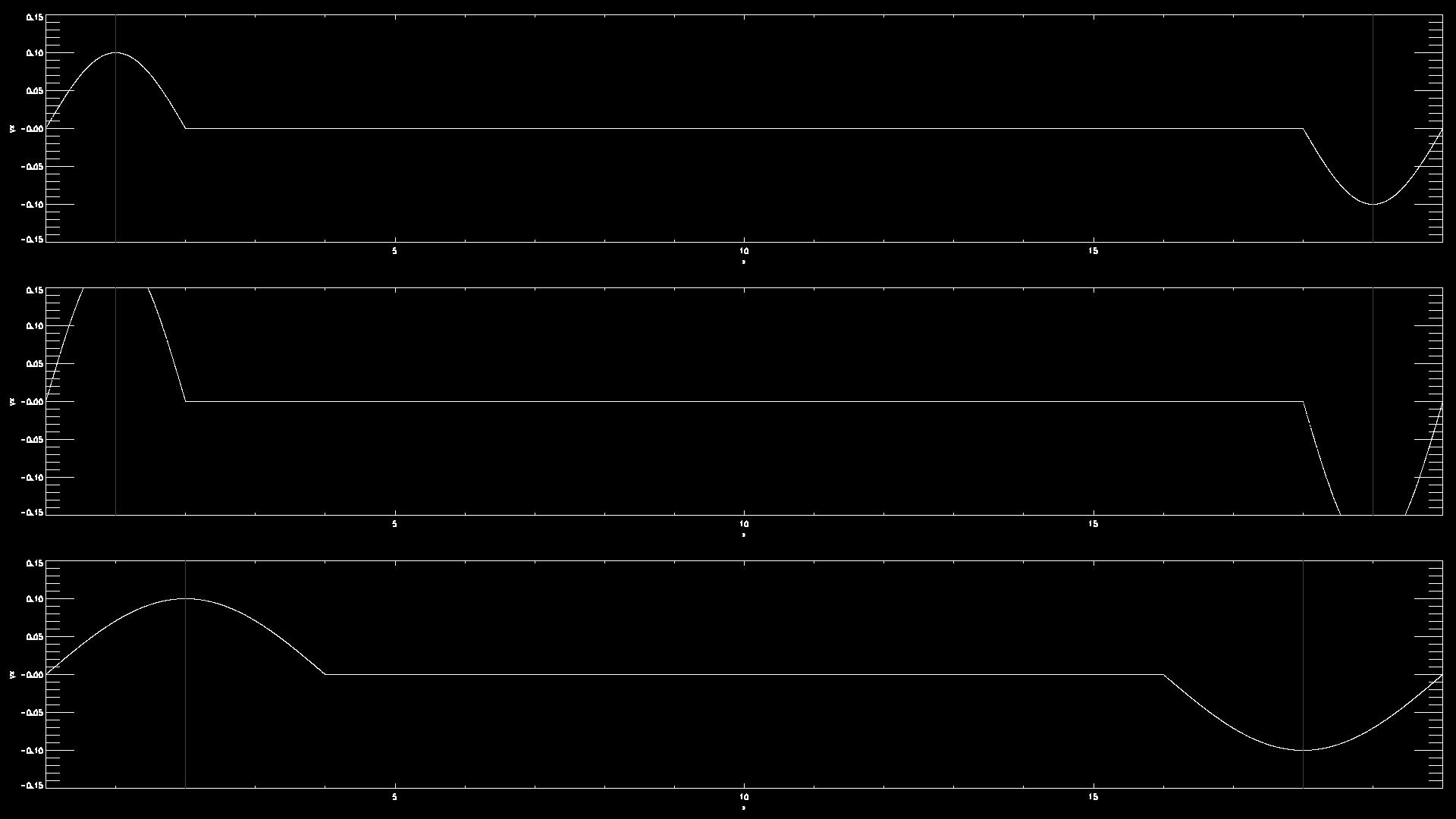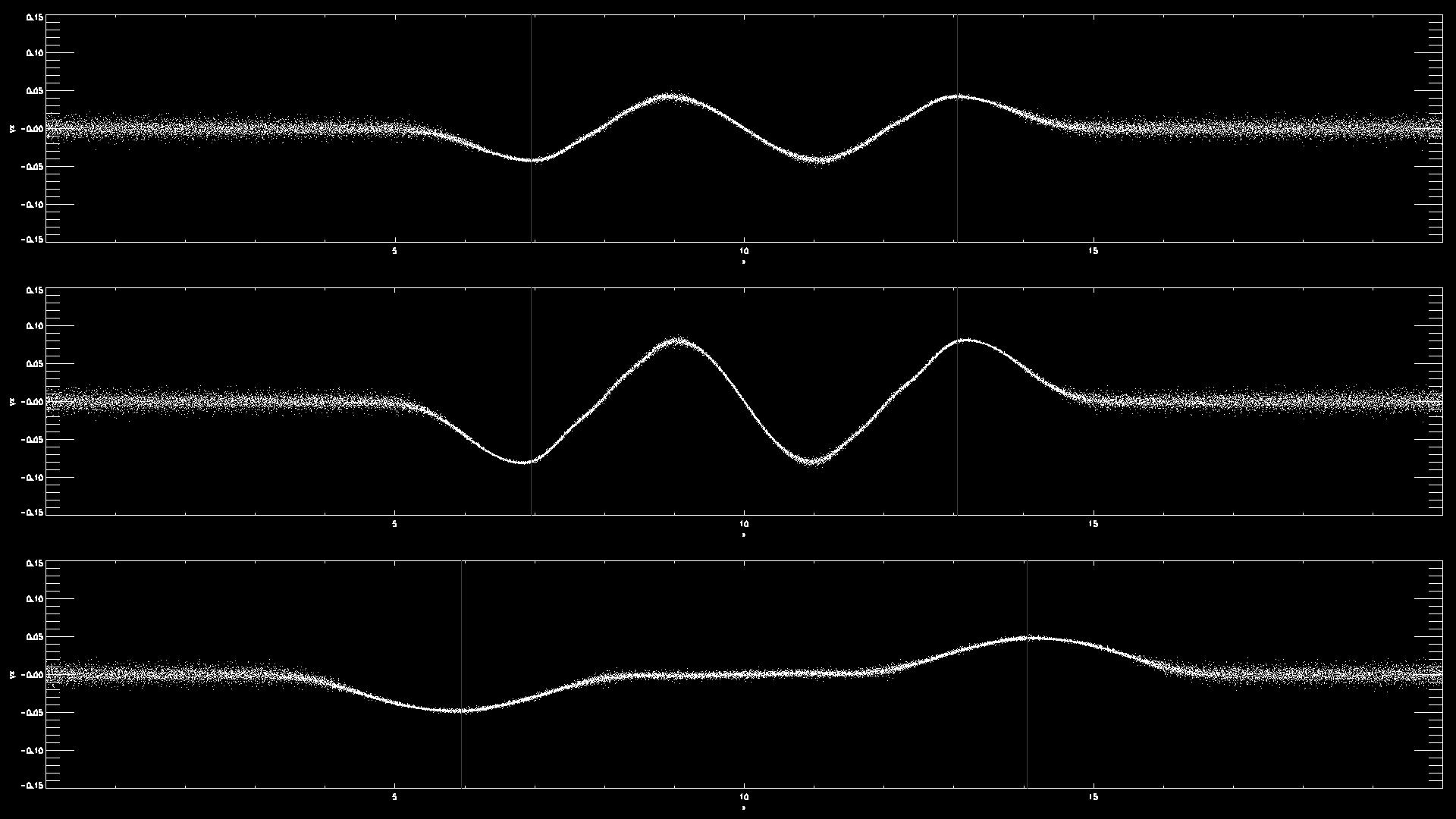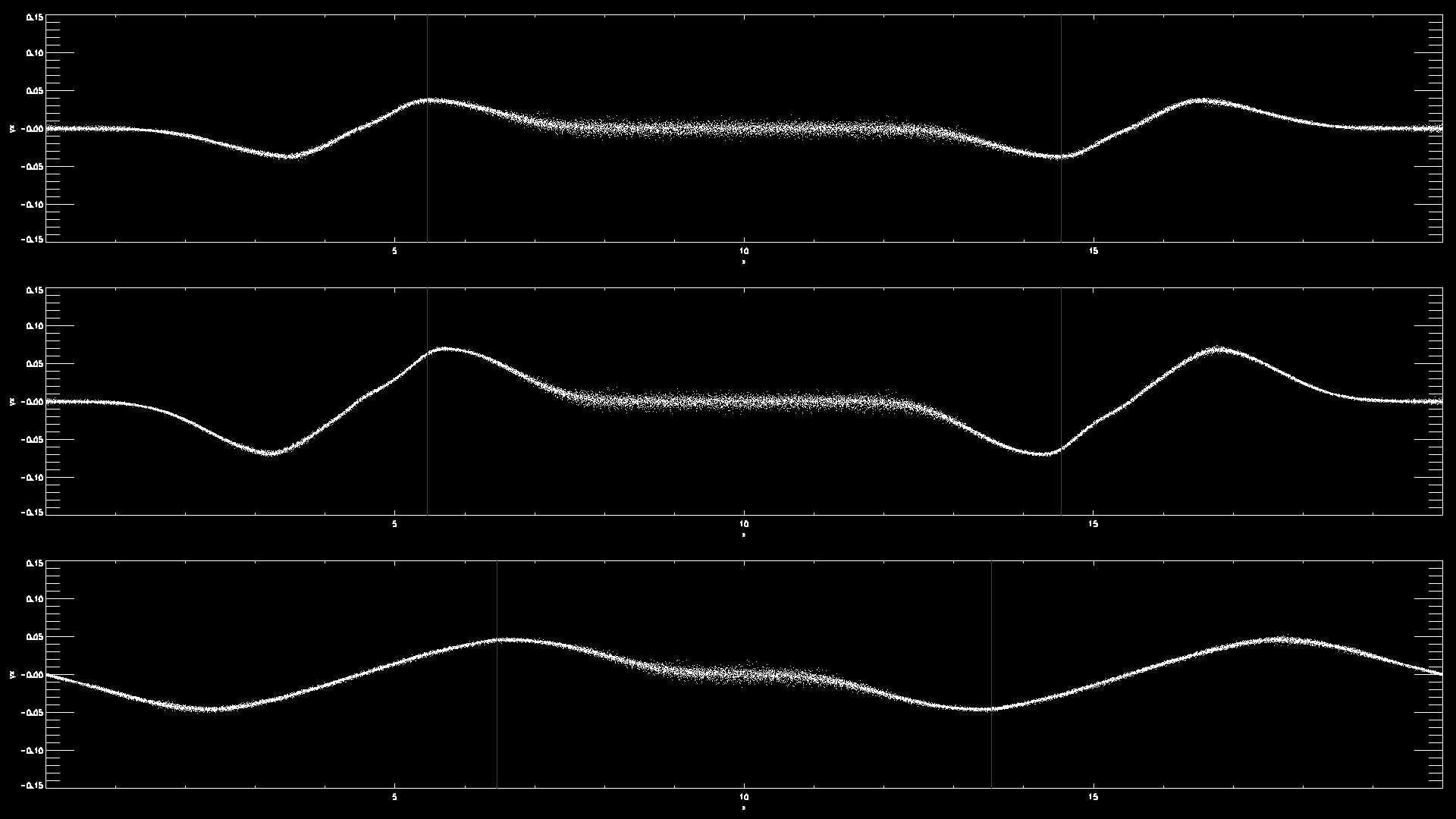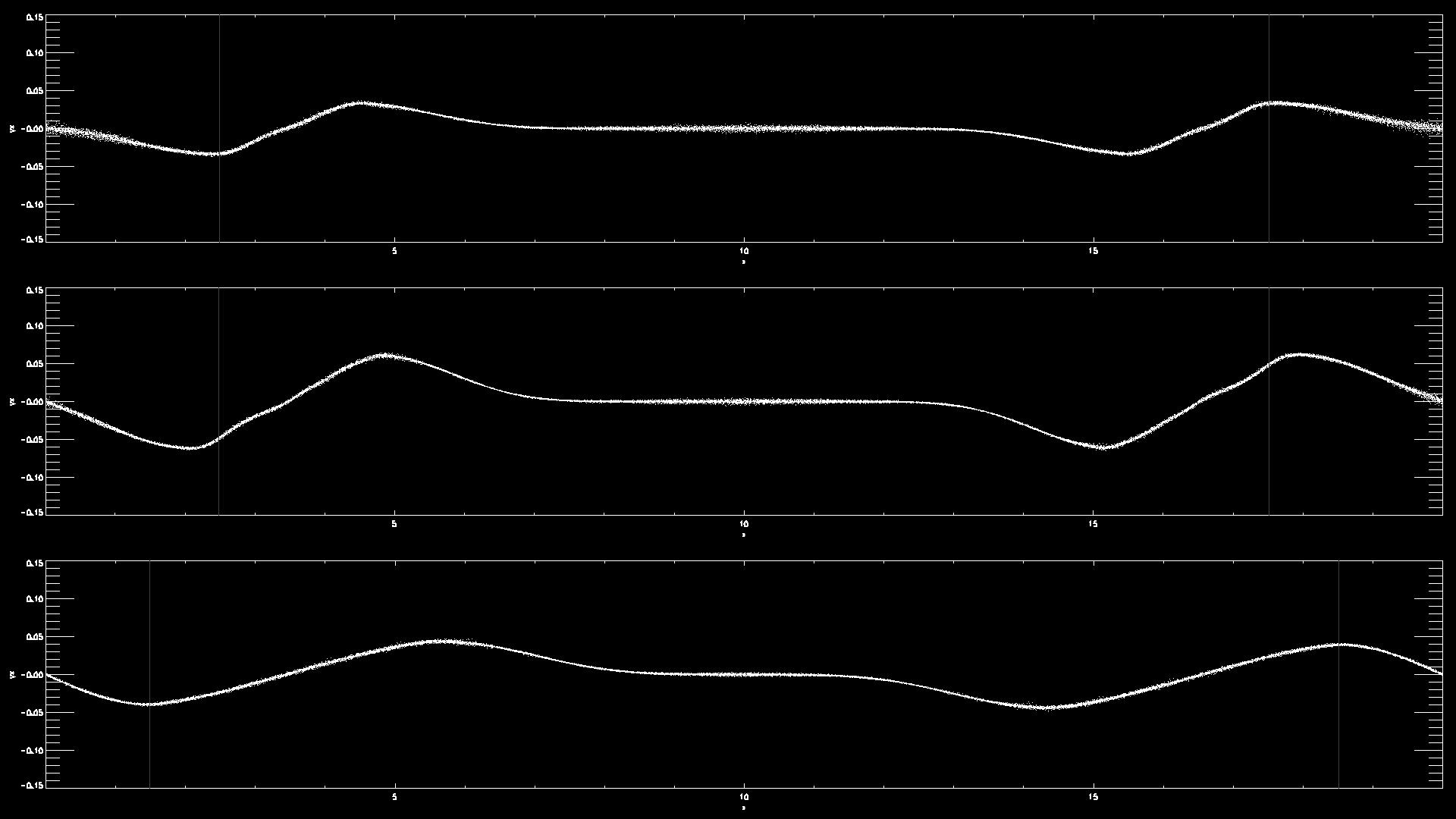
- Example using Fortran and gnuplot:
ifort -g -traceback -check all -fpe0 -o slabsetup slabsetup.f90
(this uses glass.txt from T04)
./slabsetup
- run Gadget using
slab.ic as the initial conditions file
and output as the snapshot file base in the parameter file
ifort -g -traceback -check all -fpe0 -o readsnap readsnap.f90
for file in output_???; do ./readsnap $file >$file.txt; done
gnuplot plot.plt
gv plot.ps